Key takeaways
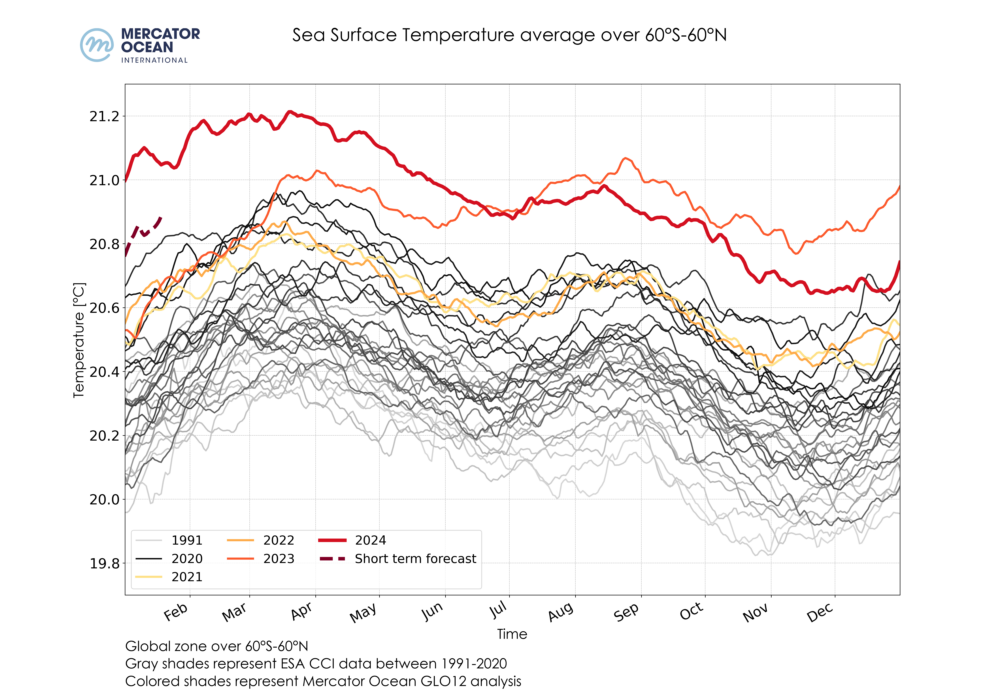
- December 2024 was the second warmest December on record since 1991, with a mean sea surface temperature of 20.67°C.
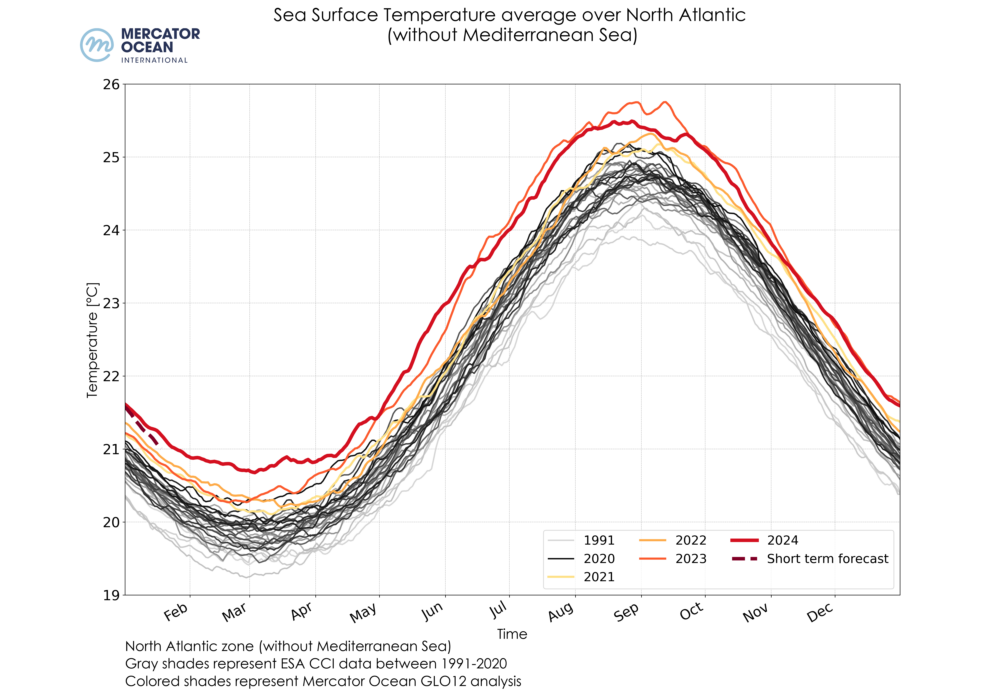
- A record monthly mean sea surface temperature was reached in the North Atlantic Ocean – 22.11°C.
- The North Atlantic Ocean had the 2nd most extreme December for marine heatwave conditions.
Sea Surface Temperature
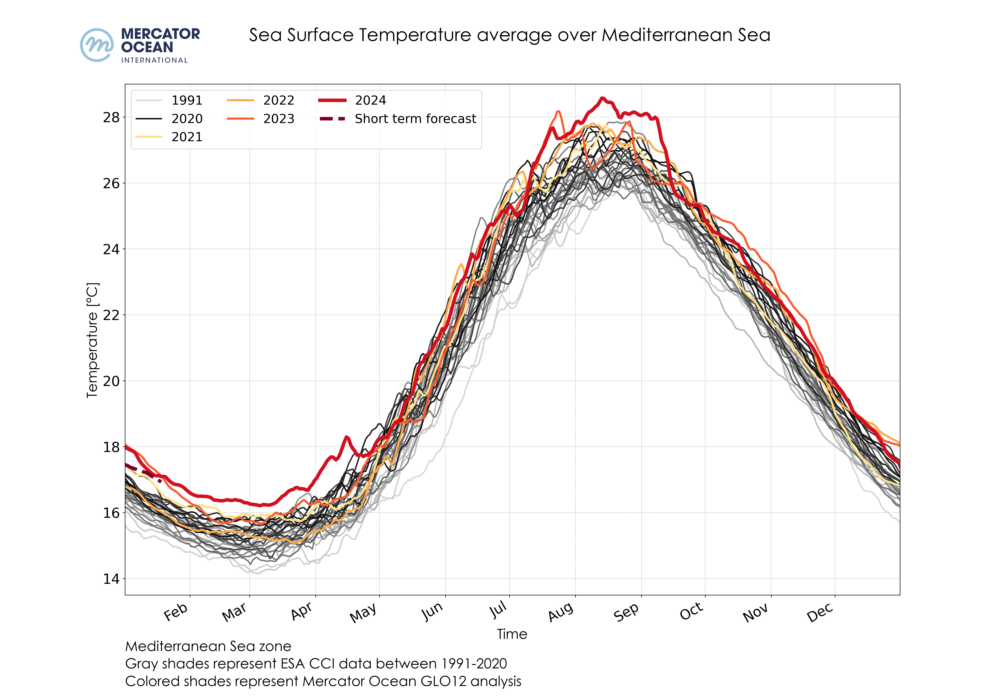
Daily sea surface temperatures averaged for the global ocean (top), the Mediterranean Sea (bottom left) and the North Atlantic Ocean (bottom right) between 1991-2020 using ESA’s Climate Change Initiative (grey shades), and between 2021-2024 (yellow, orange and red shades) + forecast (red dashed) using GLO12 analysis for December.
- December 2024 was the 2nd warmest December on record (after 2023), with a mean temperature of 20.67°C at global level (between 60°S and 60°N).
- Regionally, December 2024 was the third warmest December month for the Mediterranean Sea (after 2023 and 2022) with a mean temperature of 18.71°C. For the North Atlantic, a record monthly mean temperature of 22.11°C was reached, slightly warmer than 2023 (22.10°C).
Sea Surface Temperature Anomalies
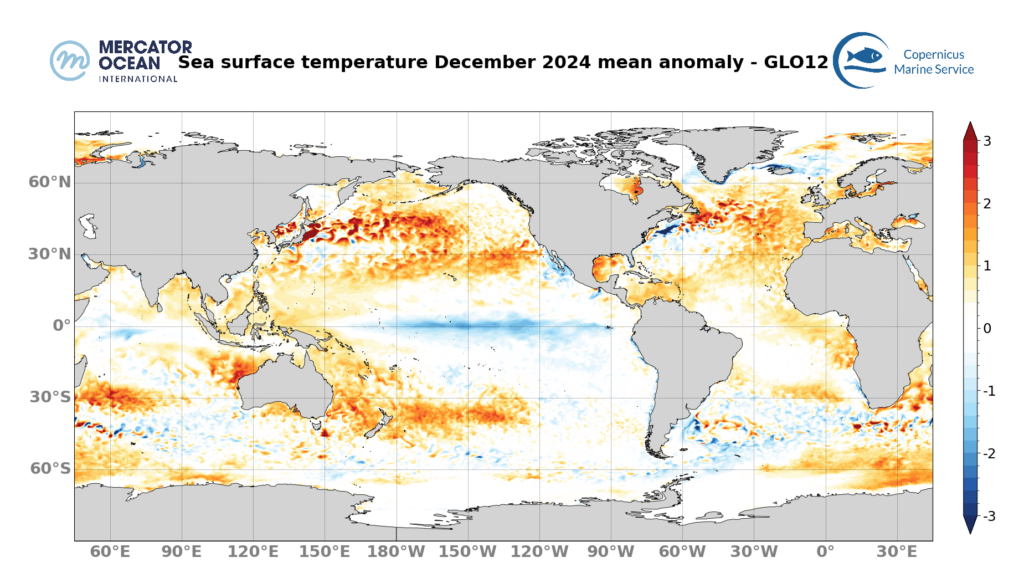
- Mean sea surface temperature (SST) anomalies for December 2024 are close to 1°C in the North Atlantic Caribbean Sea and the Mediterranean Sea.
- Anomalies are higher around New Zeeland, around Madagascar and in the North Pacific, reaching 2°C or more. In the Pacific, negative anomalies are present along the equator, reaching nearly -2°C.
Ongoing marine heatwaves: 31 December 2024
Long warming events may induce important stress on marine ecosystems. In this section are shown the ongoing marine heatwave events on December 31, and when those have initiated.
· 24.21 % of the global ocean (between 60°S and 60°N) were affected by MHWs on the 31st of December.
· The majority of these MHWs developed recently, with 17.79% of the global ocean (between 60°S and 60°N) affected by MHWs less than 1 month old and 4.02% by events between 1- and 2-month-old.
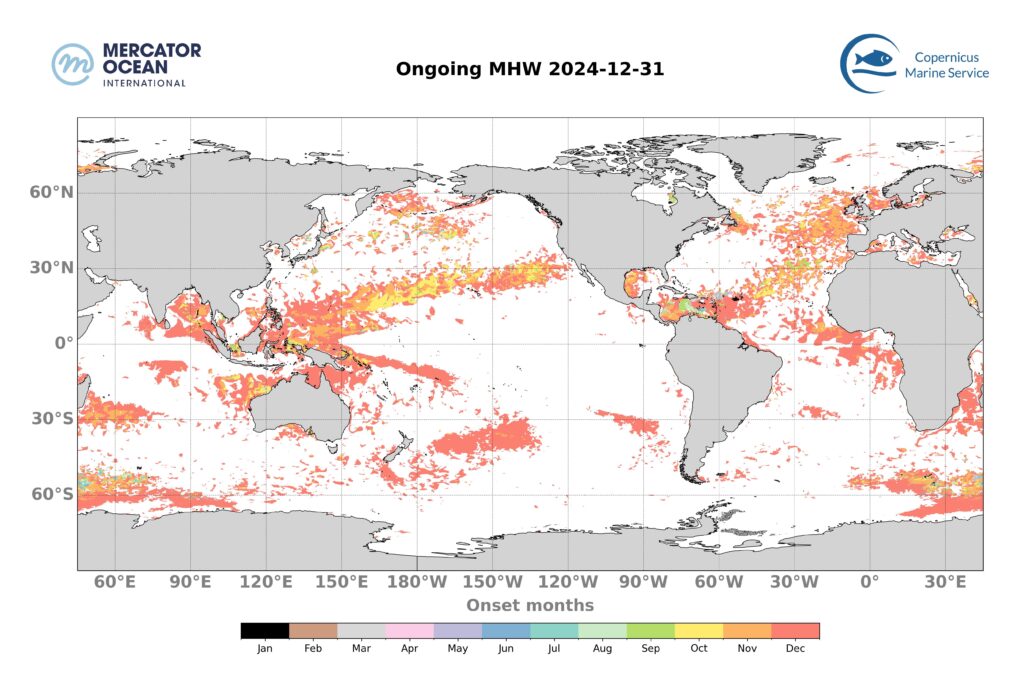
Total surface exposed to marine heatwaves (December 2023 – December 2024)
Global Ocean
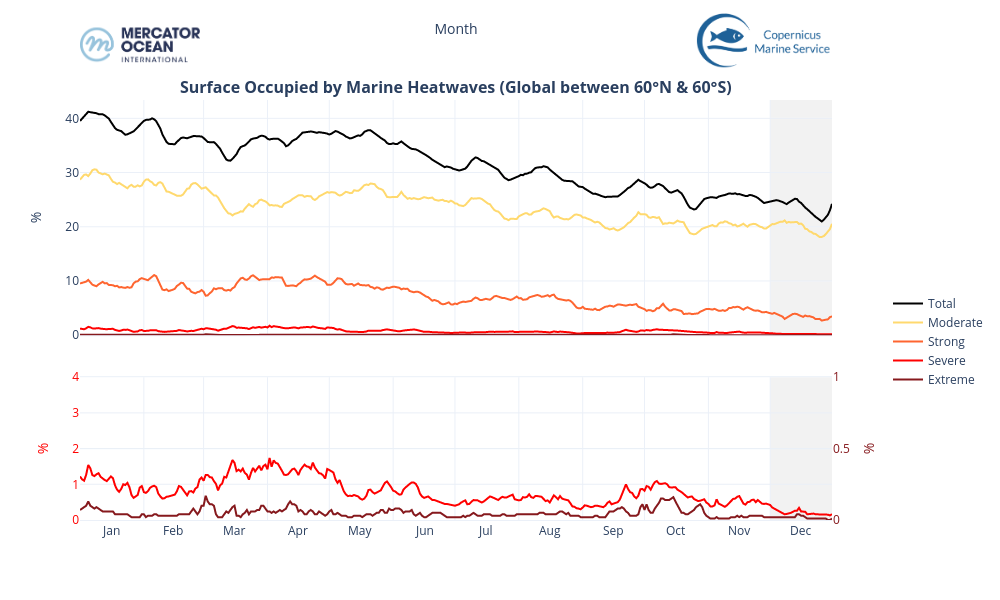
- The total surface of MHW (black line) continues a declining trend initiated at the beginning of 2024.
- In December 2024, the surface dropped from ~25% to 21% in the second half of the month, to then increase to 24% by the end of the month.
- Surface of moderate category (yellow line) follows the same pattern, ranging between 20% and 18%; whereas surface of strong category (orange line) is low and stable (less than 5%).
- For comparison, in December 2023 (the warmest December on record), MHW total extent increased from ~35% to 40% during the month (not shown).
- The maximum surface of marine heatwaves occurs during January and February, the summer season in the southern hemisphere (period of higher marine heatwave occurence), which contains a larger proportion of ocean than its northern counterpart.
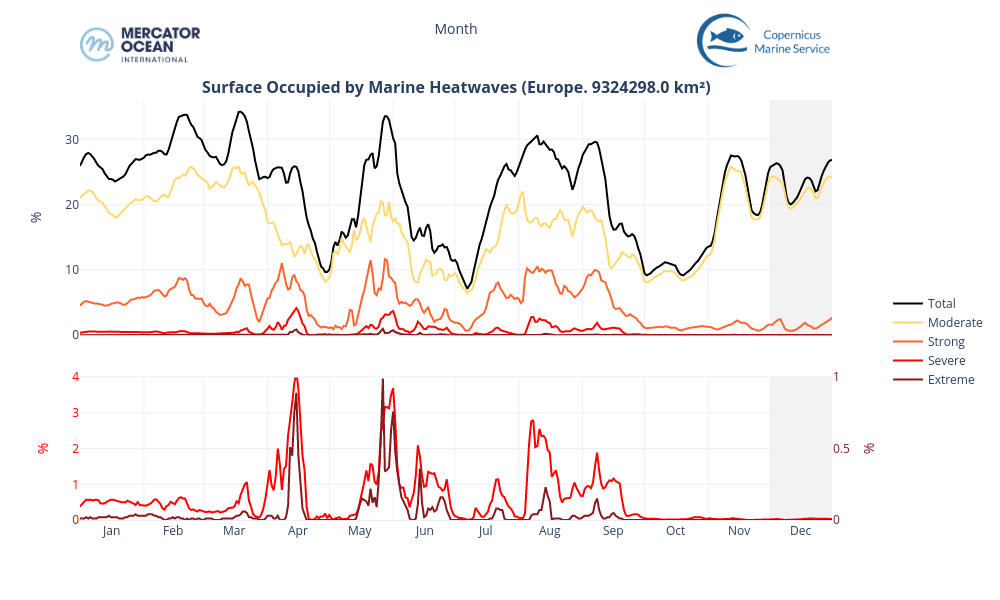
European Zone
- Mediterranean Sea and the North Atlantic eastern coast the total MHW surface fluctuates during the month between 20% and nearly 27% to end on a peak (26.86%).
- These events consist mostly of moderate events, with a small proportion of strong categories (between 0.6% and 2.7%).
Total number of marine heatwave days for December 2024
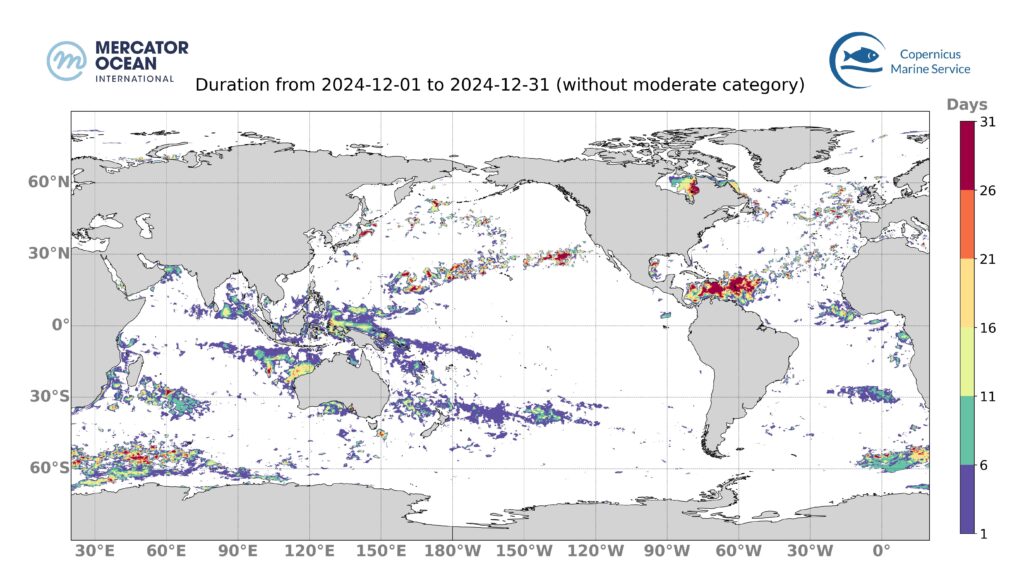
The surface of the ocean impacted by strong or higher MHW conditions for at least 1 day is 15.75 %. The impacted regions are mainly the Caribbean Sea, the southeast Asia region and the Southern Ocean south of Africa.
The surface of the ocean covered by strong or higher MHW conditions during the entire month is 0.33%. This takes place predominantly in the Caribbean region.
December Statistics
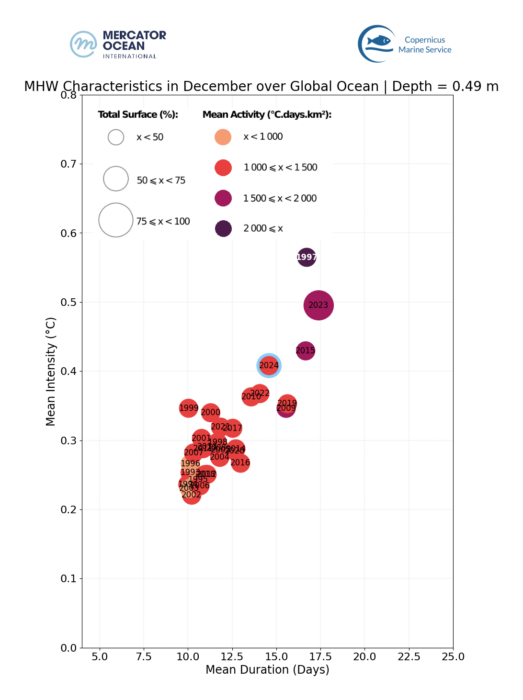
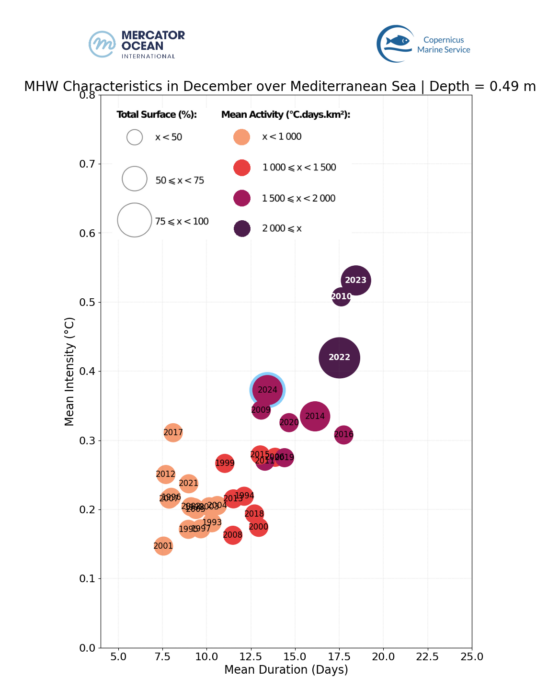
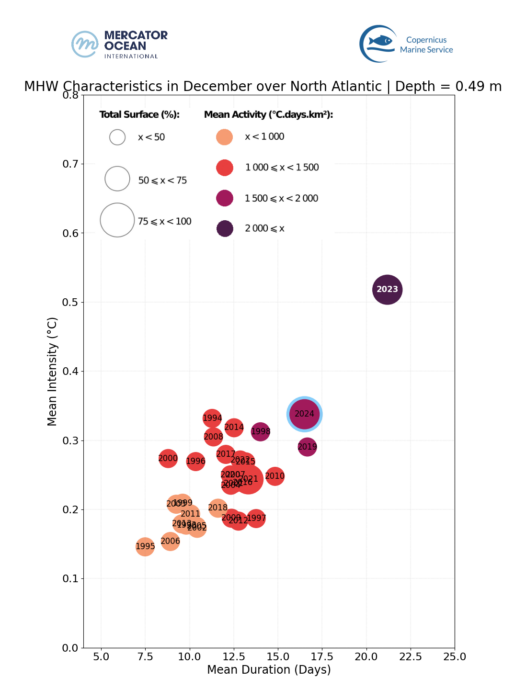
Mean duration, intensity, occupied surface and frequency of marine heatwave events in December months between 1993 and 2024 for the global ocean (left), for the Mediterranean Sea (centre) and theNorth Atlantic Ocean (right). Satelite measurements were obtained for the 0.49 m ocean surface layer.
The MHW statistics – MHW duration, intensity, occupied surface and frequency – for December 2024 are compared to all December months since 1993.
- Global ocean: December 2024 was the 3rd most extreme December month in terms of MHWs intensity (after 1997, 2023 and 2015) and the 5th most extreme December in terms of duration (after 1997, 2023, 2015, 2019 and 2009).
- Mediterranean Sea: December 2024 was moderate in terms of duration. In terms of intensity, it corresponds to the 4th most extreme December (after 2023, 2010, and 2022).
- North Atlantic Ocean: the 2nd most extreme December month, only December 2023 was more extreme.
About the bulletin
Mercator Ocean International (MOi) publishes a monthly sea surface temperature bulletin reporting on the mean temperature and marine heatwave conditions for the month just passed. It includes:
- Where an MHW is present, the time this event started,
- The timeseries showing the total surface occupied by MHWs globally and for the European region,
- The total number of days of exposure to MHW during the month (including only strong and higher intensity categories).
The results are obtained using the Copernicus Marine Service global analysis system at 1/12° of resolution.
Image citation: European Union, Copernicus Marine Service Data 2024 I © Mercator Ocean
All images in this article can be used freely and should be cited with the information above.