This time of year, maximum and minimum sea ice coverage is expected in the Arctic and in the Antarctic, respectively. At opposite seasonal cycles, the north and south poles reach their freezing and melting peaks every year between February and March. Scientists at Mercator Ocean International (MOi) have been monitoring seasonal sea ice changes using the global ocean analysis and forecast, and reanalysis systems. The beginning of February 2024 shows similar conditions in sea ice extent and volume to last year’s, for both polar regions.
Antarctic Sea Ice Extent
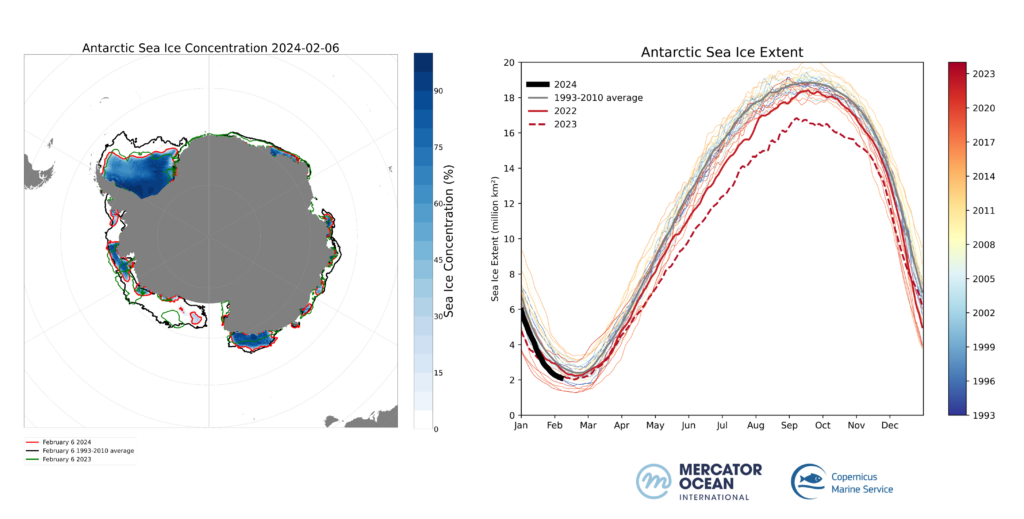
As of the 6 of February 2024, Antarctic Sea ice extent is detected at 2.11 million square kilometres, 0.66 million square kilometres below the long-term average for the same day of the year (1993-2010). These numbers seem to follow the minimum extent found in Antarctica in 2023 (figure 1 right). Particularly, an important lack of sea ice is modelled in the South-eastern part of the Pacific (Bellingshausen and Amundsen seas)(figure 1 left).
Arctic Sea Ice Extent
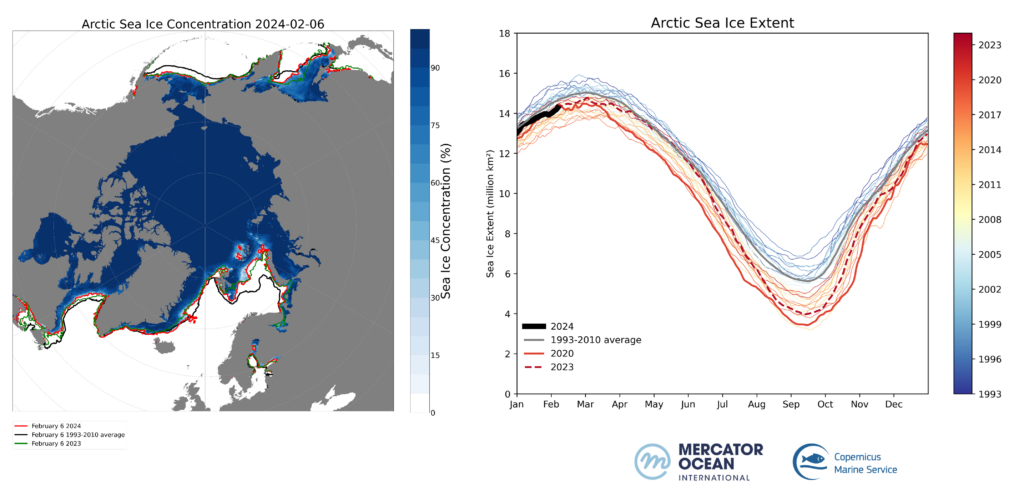
For the same date, the Arctic Sea ice extent lies at 14.27 million km² (figure 2 left). Similar conditions as in 2023 for this time of the year, where a large lack of sea ice is seen in the Barents Sea bordering the Arctic (figure 2 right).
Arctic and Antarctic Sea Ice Volume
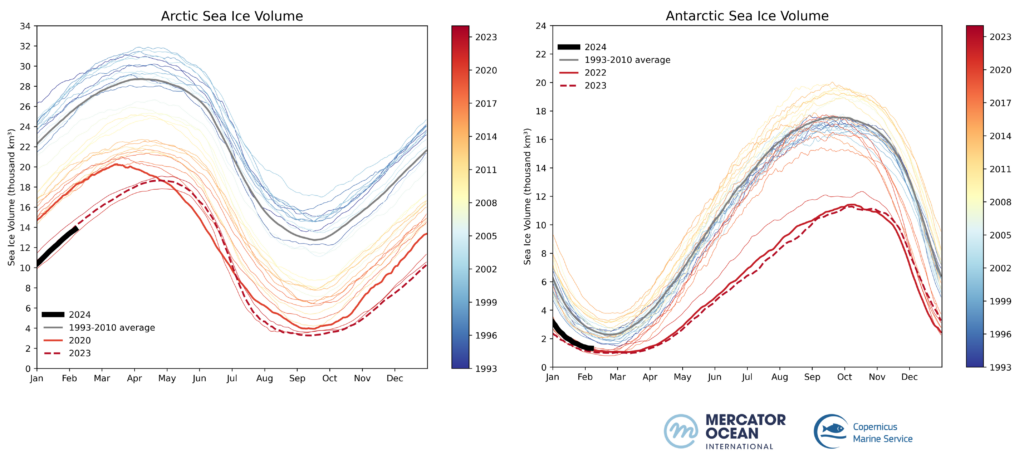
According to the global ocean physics and reanalysis system at MOi, sea ice volume in the Arctic and in the Antarctic is also repeating last years’ trend. Sea ice volume in the Arctic and the Antarctic currently sits at 13.81 thousand km³ and 1.32 thousand km³ respectively (figure 3).
The year 2023 marked record lows for both minimum and maximum sea ice extent in the Antarctic, with February showing the lowest ever observed extent since the beginning of satellite record (1979). In the Arctic, maximum sea ice extent was considered the fifth lowest.
