Key takeaways
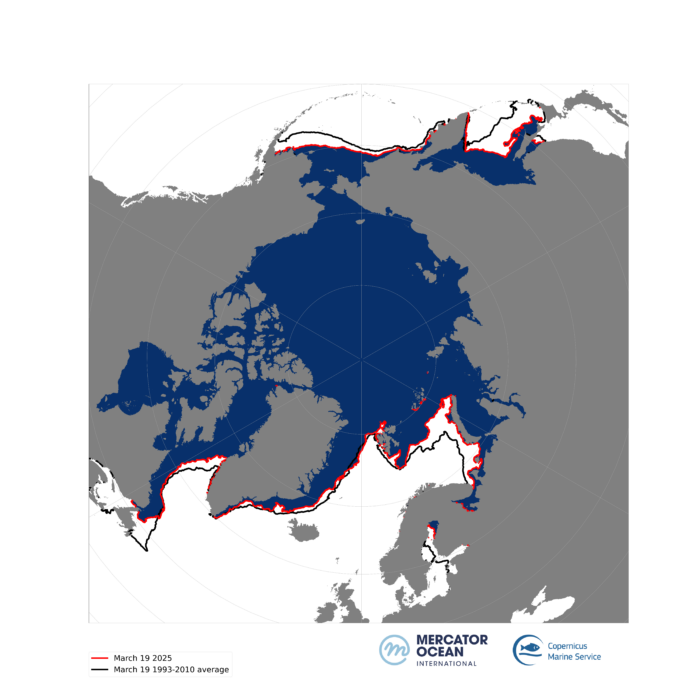
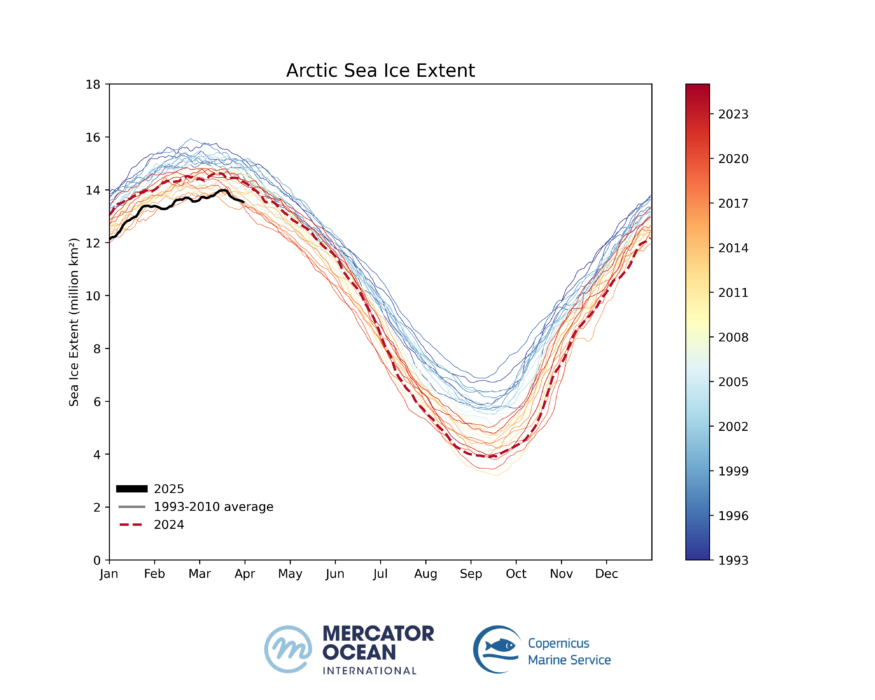
- Sea ice in the Arctic region has likely reached maximum extent on 19 March 2025, as one of the lowest extents since 1993.
- The recorded area of 13.98 million km² of sea ice represents a 6% loss compared to the long-term average.
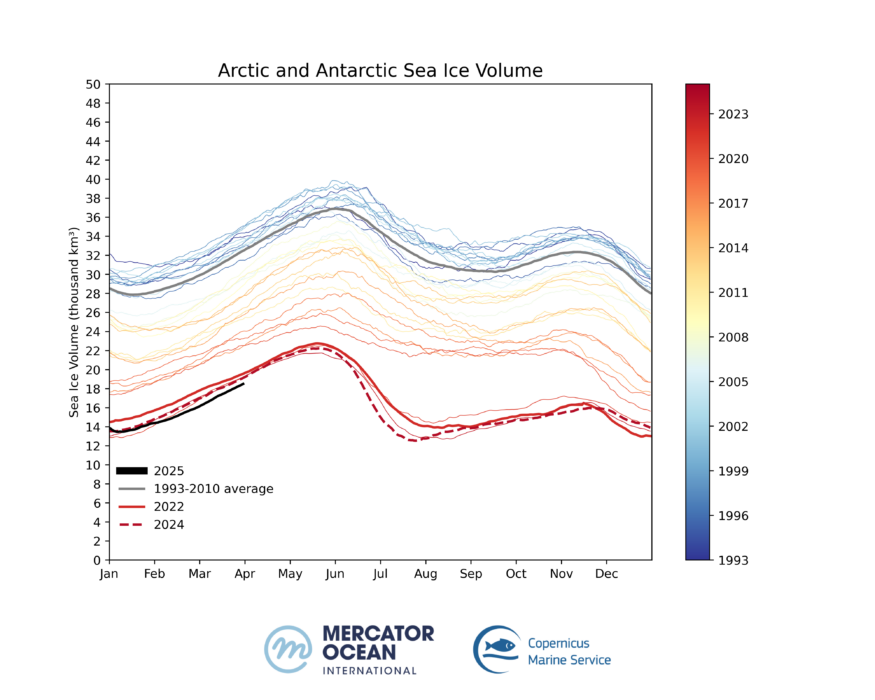
- Sea ice volume has been at a record low since the beginning of the year and on March 19 reached 16.61 thousand km³ – a 35% drop compared to the average 1993-2010.
- Global sea ice reaches continuously lower extents each year. 2025 is another record low for global sea ice volume.
Arctic sea ice at one of the lowest extents
Sea ice extent in the north polar region has seen a near breaking record-low in the first quarter of 2025. The maximum area occupied by sea ice has fallen to 13.98 million km² – a value that follows closely the previous record lows of 2017, 2016 and 2018 – back to values below 14 million km ².
Compared to the long-term average 1993-2010 for March, major deficits are observed in all the marginal areas of the Atlantic and Pacific regions, particularly in the Barents Sea, the Gulf of St. Lawrence and in the Sea of Okhotsk.
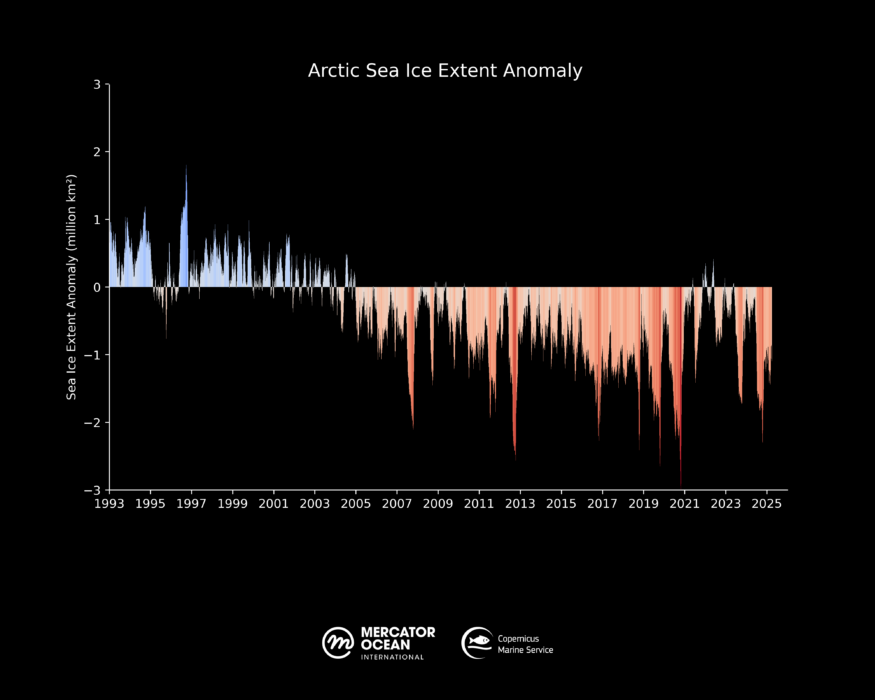
Figure 2: The 1993-2025 Arctic Sea ice extent daily anomaly (using 1993-2010 average as a reference period).
Arctic Sea Ice Volume
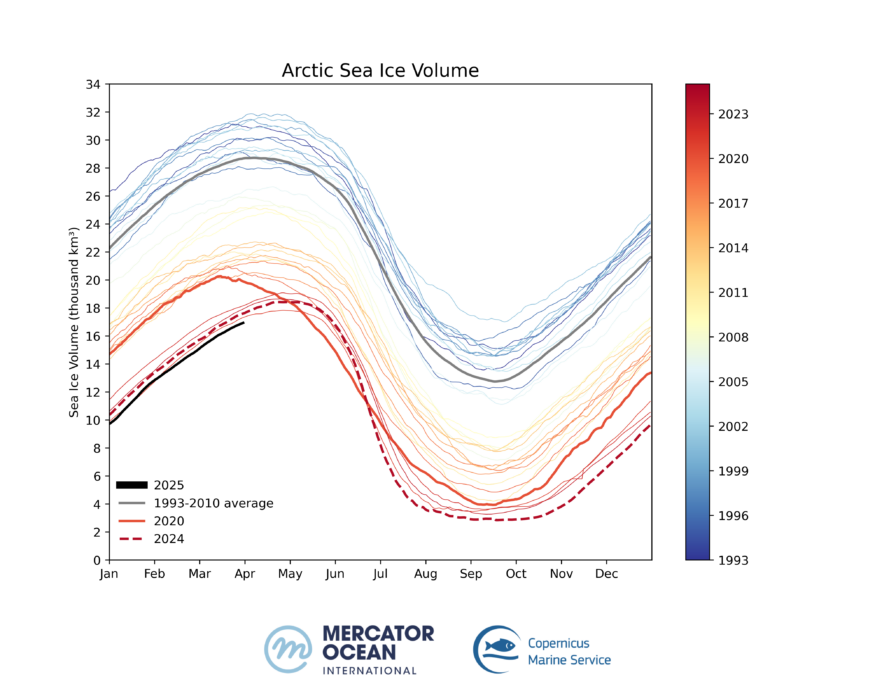
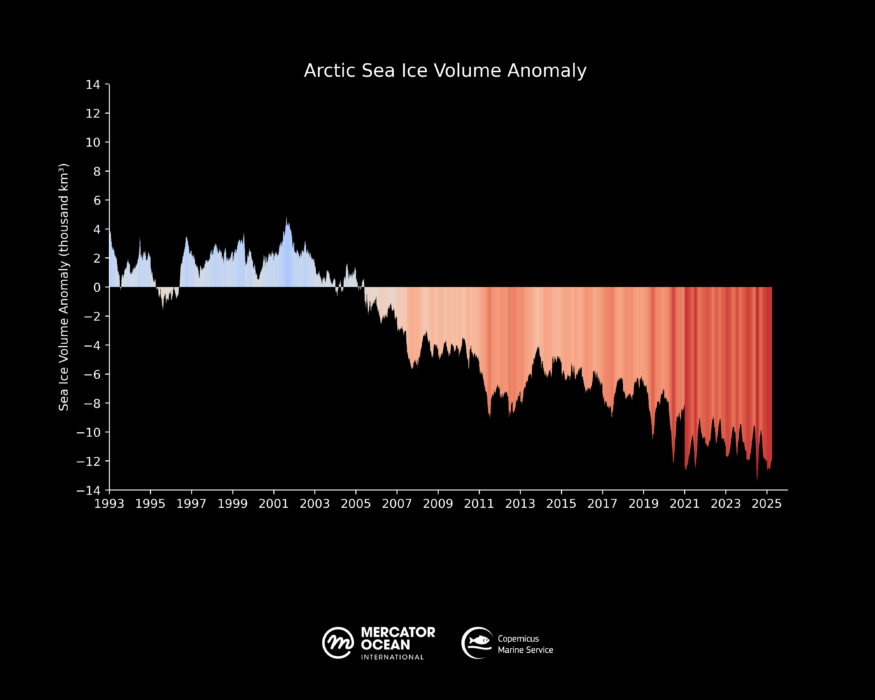
Another record low for sea ice volume
Since 1993, the sea ice volume in the Northern Hemisphere has been decreasing steadily, breaking records year after year. Although not yet at its maximum level, (sea ice minimum and maximum volumes are attained later than sea ice minimum and maximum extents)19 March 2025 registers another record low sea ice volume for this time of the year, at 16.61 thousand km3. This represents a 35% loss of sea ice volume in the Arctic compared to the reference period 1993-2010 (25.50 thousand km3).
Global Sea ice
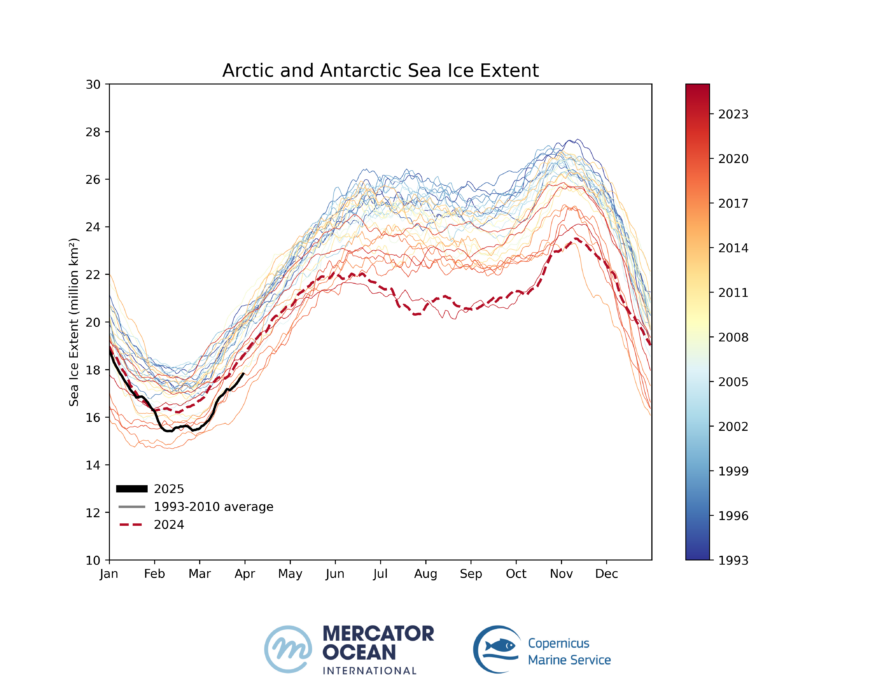
Sea ice cover at both high boreal and southern latitudes is close to a new record low, with the start of 2025 reaching a minimum extent of 15.40 million km ² on February 12th – 1.93 million km² less than the average for the same time of the year.
At the start of 2025, the global volume of sea ice followed the same trajectory as in 2024, with a new record minimum volume at 13.46 thousand km3 on 7 January 2025 – 52% less than the 1993-2010 average (figure 4).
Definitions:
- Sea ice concentration – percentage of sea ice cover within the data grid cell.
- Sea ice extent – area covered by a significant amount of sea ice, at least 15% sea ice concentration (km²).
- Sea ice volume – derived from sea ice concentration and sea ice thickness integrated over a respective area (km ³).
Notes:
Products and data used:
- GLORYS12V1 global ocean eddy-resolving (1/12° horizontal resolution, 50 vertical levels) reanalysis covering the altimetry (1993 onward). https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00021
- The Operational Mercator global ocean analysis and forecast system at 1/12 degree. https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00016
Credits:
*Image citation: European Union, Copernicus Marine Service Data 2025 I © Mercator Ocean
All images in this article can be used freely and should be cited with the information above.